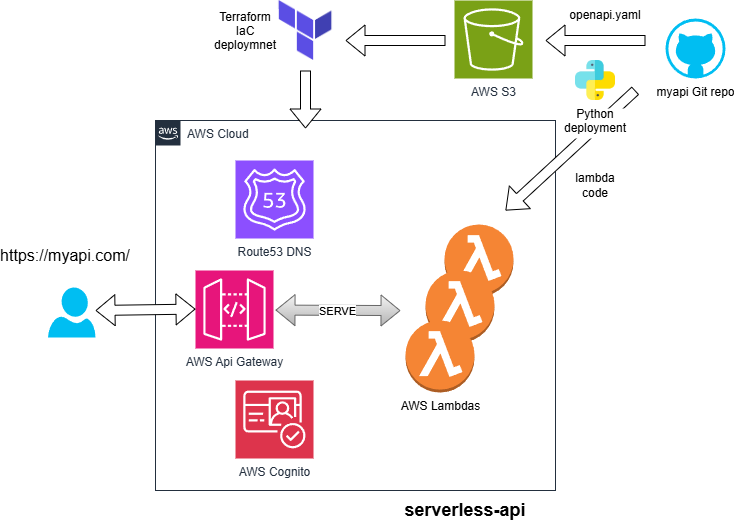
Overview
This tutorial shows how to build a dynamic, maintainable serverless HTTP API using:
- AWS Lambda for function execution
- API Gateway (HTTP API) for routing
- OpenAPI for declarative route definitions
- SSM Parameter Store for dynamic dependency resolution
- Terraform for infrastructure provisioning
The key idea is to deploy Lambda functions and API Gateway separately, using nicknames and SSM parameters to wire them together without hardcoding ARNs or requiring manual updates.
⚠️ This is not a REST API. You are deploying a Lambda-backed HTTP API — lightweight, event-driven, and version-agnostic.
1. Why Decouple API and Lambda?
Traditionally, you must:
- Define each API route manually
- Hardcode Lambda ARNs into API Gateway integrations
This couples infra too tightly. Instead:
- OpenAPI defines routes
- Lambdas are deployed independently
- Terraform wires them together by looking up ARNs from Parameter Store
This enables testing, hotfixing, and gradual rollout without redeploying the API or hardcoding anything.
2. Define the OpenAPI Spec
Create a file like openapi/demo-api/openapi.yaml:
openapi: 3.0.3
info:
title: Demo API
version: 1.0.0
description: A simple demo API with basic endpoints for testing.
paths:
/status:
get:
summary: Health check
x-lambda-nickname: status
responses:
'200':
description: OK
content:
application/json:
example:
status: ok
version: 1.0.0
/echo:
post:
summary: Echo the posted JSON back
x-lambda-nickname: echo
requestBody:
required: true
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
responses:
'200':
description: Echoed input
content:
application/json:
example:
input:
message: hello
received_at: "2025-05-02T12:34:56Z"
/time:
get:
summary: Return current server time
x-lambda-nickname: time
responses:
'200':
description: Current timestamp
content:
application/json:
example:
timestamp: "2025-05-02T12:34:56Z"
The custom
x-lambda-nicknametag defines which Lambda function handles this route.
3. Deploy the Lambdas
python scripts/deploy_lambda.py echo
This script:
- Installs dependencies (if any)
- Creates a ZIP
- Publishes the Lambda and gets its versioned ARN
- Stores the unversioned ARN in SSM under:
/iac/lambda/echo/runtime
Repeat for each Lambda function used in the OpenAPI spec.
4. Upload the OpenAPI Spec
python scripts/deploy_openapi.py demo-api
This script:
- Uploads the OpenAPI YAML to S3 (bucket resolved via
/iac/s3-bucket/demo-api/runtime) - Writes a pointer to the file in SSM:
/iac/openapi/demo-api/runtime
Terraform can now resolve the OpenAPI spec dynamically.
5. Terraform: Serverless API Component
The Terraform module:
- Reads the OpenAPI pointer from SSM
- Parses the spec
- Resolves each
x-lambda-nicknameto its Lambda ARN (unversioned) - Wires up API Gateway routes and integrations accordingly
If enable_custom_domain = true, it also:
- Creates a DNS-validated certificate
- Sets up a custom domain like
demo-api.usekarma.dev
Example Result
After deployment, you’ll have a working endpoint like:
POST https://demo-api.usekarma.dev/status
Calling that route will invoke the Lambda currently deployed under the nickname status.
Quickstart
To get started quickly with this pattern:
- Follow the Serverless API Quickstart
- Use the aws-openapi repo to manage your spec and Lambda code
- Use aws-config and aws-iac to manage config and infra
What’s Next
Part 2 will show how to:
- Protect routes with Cognito authorizers
- Keep the same nickname-based resolution
- Attach authentication dynamically from configuration
Stay tuned.